Find out more about Oticon Zeal

Types of hearing loss
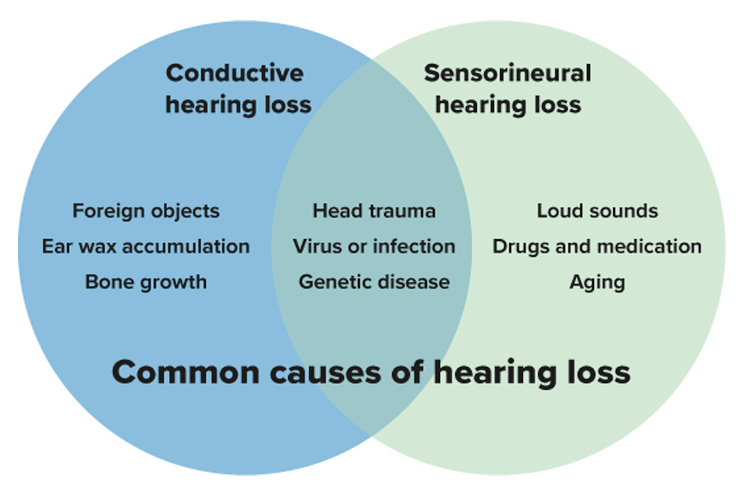
There are three types of hearing loss: sensorineural, conductive, and mixed.
When it comes to treating hearing loss, it's important to understand the differences so you can get a treatment option that works for you.
What are the main types of hearing loss?
The main types of hearing loss are differ based on which part of the ear is damaged:
- Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear or hearing nerve. This prevents the damaged area from properly transmitting sound to the brain.
- Conductive hearing loss is caused by damage to the outer and/or middle ear and, in some cases, it is medically treatable.
- Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss

Self-assessment: Do I need a hearing test?
Just answer the four questions below to see whether you should consider getting a hearing test.
Your Result:
You would benefit from a hearing test
Your answers indicate that you experience symptoms of hearing loss. We strongly recommend booking a hearing test in one of our clinics.
The result is an indication. An in-person hearing test can determine if you have a hearing loss.
Book your free hearing test:
Your Result:
It seems you’d benefit from a hearing test
Your answers indicate that you experience some symptoms of hearing loss. We recommend booking a hearing test in one of our clinics.
The result is an indication. An in-person hearing test can determine if you have a hearing loss.
Book your free hearing test:
Your Result:
It cannot be determined whether you’d benefit from a hearing test
Your answers do not indicate that you experience symptoms of hearing loss. However, if you experience trouble hearing, we recommend booking a hearing test in one of our clinics.
The result is an indication. An in-person hearing test can determine if you have a hearing loss.
Book your free hearing test:
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (or sensorineural deafness) is the most common type of hearing loss. For people experiencing sensorineural hearing loss, sounds may be unclear or difficult to hear. Voices in conversation may be distorted, and it might seem like others are mumbling.
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss
- The natural ageing process (age-related hearing loss / presbycusis)
- Excessive exposure to noise (noise-induced hearing loss).
Treating sensorineural hearing loss
This type of hearing loss is often treated with hearing aids.

Conductive hearing loss
Sound travels from the outer/middle ear to the inner ear. But if there's a disruption along its path, this can result in conductive hearing loss.
Causes of conductive hearing loss
This type of hearing loss can also be caused by an obstruction in the ear canal, like ear wax or liquid preventing sound from reaching the eardrum.
Treating conductive hearing loss
Treatment for conductive hearing loss includes: ear wax removal, and medical and surgical treatments.
Learn how Katie came to accept her hearing loss
“If I was to give someone with hearing loss advice, I would just say life doesn’t stop there – you can do anything.
“If you’re struggling with your hearing, don’t hide behind it – go and get your ears tested because you don’t know what you’re missing out on.”
| Audio | Visual |
| Admitting to yourself that you have a hearing loss is probably the hardest thing. I didn’t start wearing hearing aids until I was about 21 I think. | Caption reads: Katie – model and salon owner. Katie is sitting against a rack of weight bars in a gym. Zoom in on Katie’s head from behind as she’s pulling up her hair into a ponytail so that we can see her behind-the-ear hearing aid. |
| I got given my first pair of hearing aids about 18. | Zoom out – Katie is walking across the gym floor, pausing to pick up a gym bag. |
| These hearing aids that I’ve been given by Hidden Hearing, they’re just amazing. | Katie is sitting against a rack of weight bars in the gym |
| The technology is incredible. | Zoom in on Katie’s head from behind as she’s pulling up her hair into a ponytail so that we can see her behind-the-ear hearing aid. |
| Now, they are just so, so small for the power that they have; they’re incredible really. They’re literally minute and they sit right behind my ear, so even if I was to wear my hair up, you can barely even see them, which is brilliant for me. When I went to Hidden Hearing for my hearing test, the test was so thorough, so that was really impressive. | Katie is sitting against a rack of weight bars in a gym, talking to the interviewer who is out of shot. She is removing her hearing aid from her left ear and presenting it to us in the palm of her right hand, to highlight how small it is. She is now putting her hearing aid back in. Katie is jumping up onto a box, stepping down and then jumping back up again. |
| Even now, after 11/12 years I probably would say that I haven’t completely accepted it still, and I don’t think it’s something I ever will. But the more I try to, the easier things become, and the more people you tell, the easier things become as well. If I was to give someone with hearing loss advice, I would just say life doesn’t stop there – you can do anything. | Katie is putting her hands in to a bucket of chalk, now she is lifting a weighted barbell up to her shoulders. Katie is doing chin ups on a bar. Katie is using a cross-trainer bike. |
| It might be a little harder for you, but it will make you a stronger person for it. If you’re struggling with your hearing, don’t hide behind it – go and get your ears tested because you don’t know what you’re missing out on. | Katie is dropping a weighted barbell, is climbing a rope in the gym and is skipping using a skipping rope. |
| For more information on Hidden Hearing, visit their website. | The screen fades to white and the Hidden Hearing logo appears. |
Other types of hearing loss
There are other ways to describe hearing loss types. For example:
– High- or low-frequency: Indicates whether you are unable to hear high- or low-pitched sounds (i.e. high-frequency hearing loss means you cannot hear high-pitched sounds)
High-frequency hearing loss
Low-frequency hearing loss
Bilateral hearing loss
Unilateral hearing loss
– Progressive or sudden hearing loss: Indicates whether the hearing loss happens quickly or gradually over time
– Acquired or congenital: Indicates whether your hearing was present at birth or acquired at a later stage in life
Congenital hearing loss
Genetic hearing loss


Tinnitus: ringing in the ears
Tinnitus is a ringing, buzzing, whistling, roaring, hissing sound in the ear that only you can hear. Tinnitus affects about 13% of people in the UK, or 1 in 8. It's often one of the first signs of hearing loss.
The most common cause is exposure to excessive noise, which damages the tiny hair cells in the inner ear. The sound of tinnitus is the result of your brain trying to compensate for the loss of hair cells. The brain misinterprets the reduced signals from the ear, resulting in a perception of sound, or tinnitus.
Sources
1. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tinnitus/symptoms-causes
2. David M Baguley, Mechanisms of tinnitus, British Medical Bulletin, Volume 63, Issue 1, October 2002, Pages 195–212, https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/63.1.195
3. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/hearing-aids/hearing-loss
4. https://hearinghealthfoundation.org/types-of-hearing-loss




